Object Steam Generators Nuclear
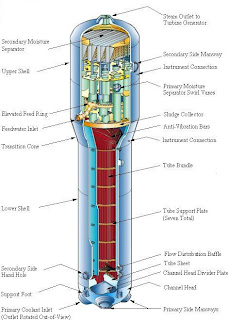
Steam generators are heat exchangers used to convert water into steam from heat produced in a nuclear reactor core. They are used in pressurized water reactors between the primary and secondary coolant loops.
In commercial power plants steam generators can measure up to 70 feet in height and weigh as much as 800 tons. Each steam generator can contain anywhere from 3,000 to 16,000 tubes, each about three-quarters of an inch in diameter. The coolant (treated water), which is maintained at high pressure to prevent boiling, is pumped through the nuclear reactor core. Heat transfer takes place between the reactor core and the circulating water and the coolant is then pumped through the primary tube side of the steam generator by coolant pumps before returning to the reactor core.
Steam Generators Nuclear System
This is referred to as the primary loop. That water flowing through the steam generator boils water on the shell side to produce steam in the secondary loop that is delivered to the turbines to make electricity. The steam is subsequently condensed via cooled water from the tertiary loop and returned to the steam generator to be heated once again. The tertiary cooling water may be recirculated to cooling towers where it sheds waste heat before returning to condense more steam. Once through tertiary cooling may otherwise be provided by a river, lake, or ocean. This primary, secondary, tertiary cooling scheme is the most common way to extract usable energy from a controlled nuclear reaction.
These loops also have an important safety role because they constitute one of the primary barriers between the radioactive and non-radioactive sides of the plant as the primary coolant becomes radioactive from its exposure to the core. For this reason, the integrity of the tubing is essential in minimizing the leakage of water between the two sides of the plant. There is the potential that, if a tube bursts while a plant is operating, contaminated steam could escape directly to the secondary cooling loop. Thus during scheduled maintenance outages or shutdowns, some or all of the steam generator tubes are inspected by eddy-current testing.
In other types of reactors, such as the pressurised heavy water reactors of the CANDU design, the primary fluid is heavy water. Liquid metal cooled reactors such as the in Russian BN-600 reactor also use heat exchangers between primary metal coolant and at the secondary water coolant.

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar